Conceitos - Códigos em inglês
Do you know why some biochemical methane potential graphs show a step?
Understanding diauxic and its Influence on Biogas Production
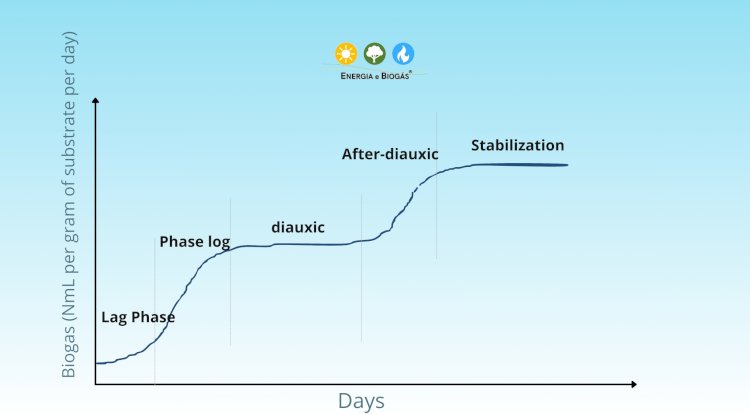
Typical Stepped Curve
This is a curious phenomenon that occurs in the anaerobic process, called diauxic. The first observation records were made by Jacques Monod in 1941, who identified diauxic growth during his experiments.
In fact, this behavior that can be observed in some curves of the result of the Biochemical Methane Potential test - BMP) of biogas production reflects the behavior of cell growth when there is multiplication of microorganisms in the anaerobic process.
During the anaerobic process, microorganisms go through an initial phase characterized as a physiological adaptation phase to nutrients and the environment they are in, called lag phase. According to Carneiro (2018), after adaptation, microorganisms initiate the fermentative and exponential growth process (considering glucose as the first source of energy, for example). This phase of exponential growth is called log phase.
In the third stage of the process, when glucose is depleted, cells enter a second lag phase, the stabilization phase that occurs between the first and second lag phases is called diauxic. At this moment, microorganisms go through another adaptation stage to consume a new substrate (degradation and obtaining energy from a new source). Then, the new growth stage is called post-diauxic (the second log phase), where cells start to metabolize ethanol (an example of a new substrate that will be degraded).
Cell Growth Phases
This adaptation behavior (lag phase), exponential growth (log phase), diauxic, post-diauxic (second lag phase), and stationary phase correspond to the beginning, middle, and end profile of the anaerobic process.
When the substrate used in the anaerobic process is heterogeneous and presents a wide variation in carbohydrate, protein, and lipid compositions, the diauxic behavior becomes more evident.

Example: Anaerobic Digestion of Substrate with Heterogeneous Composition
During BMP tests of heterogeneous substrates such as the organic fraction of municipal solid waste (OFMSW), diauxic occurs when microorganisms have "preference" for degrading (consuming) a specific element of the substrate composition, consuming it completely before starting to consume other elements of the substrate composition. For example, we can mention when glucose degradation will occur before cellulose degradation.
The typical stepped curve corresponds to the time required for inoculum adaptation (anaerobic microorganisms) to the substrate, consuming first the substrates with higher biodegradability rate and leaving the less biodegradable compounds for later.
In summary, diauxic is a term used to describe organisms that have two distinct modes of reproduction or life cycle, and these distinct modes are reflected in cellular growth (multiplication of the group of microorganisms) and are directly related to the activity of these microorganisms in substrate degradation and biomethanization. Thus, biogas production curves will exhibit stepped characteristics (diauxic).
Consulted Bibliographic References
- LIMA, H. Q. Determinação de parâmetros cinéticos do processo de digestão anaeróbia dos resíduos orgânicos de Santo André – SP por meio de testes do potencial bioquímico de metano. 2016. 153 f. Tese (Doutorado) – Centro de Engenharia, Modelagem e Ciências Sociais Aplicadas, Universidade Federal do ABC, Santo André – SP, 2016.
- LIQUORI, A. M. et al. A theoretical equation for diauxic growth and its application to the kinetics of the early development of the sea urchin embryo. Differentiation, v. 20, n. 1‐3, p. 174-175, 1981.
- Tarcio Carneiro, Alterações na parede celular e no metabolismo energético de Saccharomyces cerevisiae submetida à alta pressão hidrostática. 2018. Dissertação (Mestrado) – Universidade Federal do Espírito Santo, UFES, Brasil, 2018.
- GOMES, Carolina Scaraffuni; STRANGFELD, Martin; MEYER, Michael. Diauxie studies in biogas production from gelatin and adaptation of the modified gompertz model: Two-phase gompertz model. Applied Sciences, v. 11, n. 3, p. 1067, 2021. DOI: 10.3390/app11031067
- PÉREZ GARCÍA, M.; ROMERO GARCÍA, Luis I.; SALES MÁRQUEZ, Diego. Tecnologías anaerobias para la depuración termofílica de vertidos de destilerías vínicas. Ingeniería del agua, v. 4, n. 2, p. 7-16, 1997. DOI: 10.4995/ia.1997.2718
What do you think about this agenda? Feel free, contribute, and leave your comment.
See you soon!
Series of posts "Knowledge Nuggets"
What are granules?
About anaerobic processes, under certain conditions, there is the formation of structures consisting of anaerobic microorganisms, the anaerobic granules.
These structures (clusters of different microorganisms) enable more efficient nutrient transfer and promote the survival of the microbial community.
These densely packed clusters of microorganisms contribute to the acceleration of the anaerobic digestion process, especially in UASB reactor sludges.

The anaerobic granules are very small spheres and have a vast community of living beings. They act on the decomposition of organic matter and enable nutrient recycling.

Following the concept of "small pearls with condensed content", the Energy and Biogas Portal publishes a series of posts "Knowledge Nuggets" - small posts to contribute to the dissemination of information about the biogas production process.
Always follow our specific content about the science behind the anaerobic process and biogas production.
New posts "Knowledge Nuggets" coming soon.
See you soon!
To explore other concepts, access our Glossary.
Also access Biogas in Brazil.
Thank you and happy reading!
Check out other articles from the Energy and Biogas Portal, access:
- Biogas, Biomethane
- Anaerobic Digestion
- Biodigester - Anaerobic reactor
- Substrates - the raw material for biogas production
- What is Sulfetogenesis?
Copyright © 2018 - 2024 All rights reserved - Energy and Biogas Portal®.



 Dados, precisão e decisão: entrevista com Jing Liu
Dados, precisão e decisão: entrevista com Jing Liu A trinca de ases dos reatores CSTR
A trinca de ases dos reatores CSTR Panorama do Biogás: convite para nova atualização
Panorama do Biogás: convite para nova atualização indicações ao Prêmio Melhores do Biogás prorrogadas até dia 21fev
indicações ao Prêmio Melhores do Biogás prorrogadas até dia 21fev Plataforma Biogás Jobs
Plataforma Biogás Jobs Resíduos cítricos darão origem à maior usina de biogás do mundo
Resíduos cítricos darão origem à maior usina de biogás do mundo CGOB: Quem vai pagar a conta da descarbonização?
CGOB: Quem vai pagar a conta da descarbonização? A eficiência exergética do biogás
A eficiência exergética do biogás



